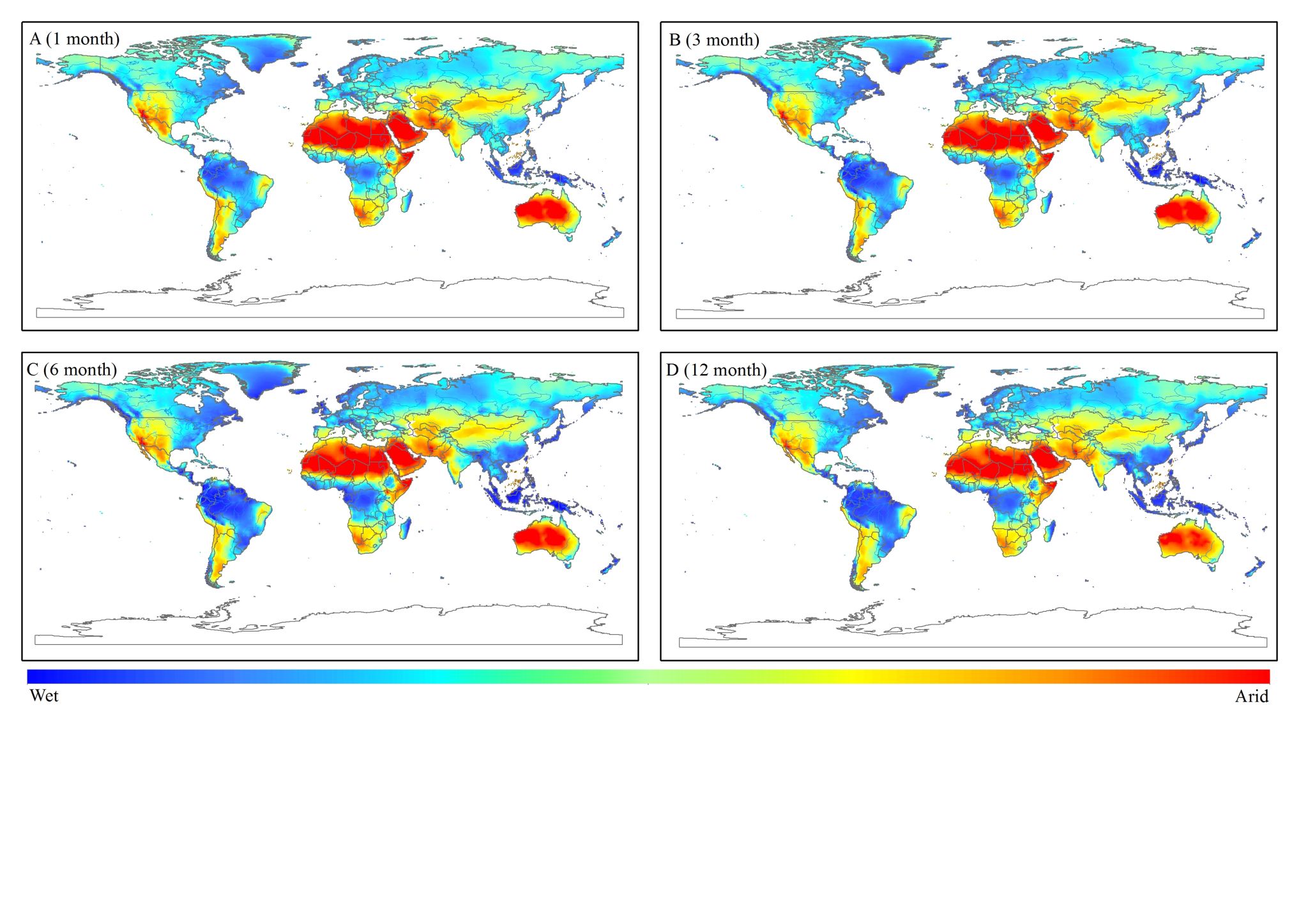
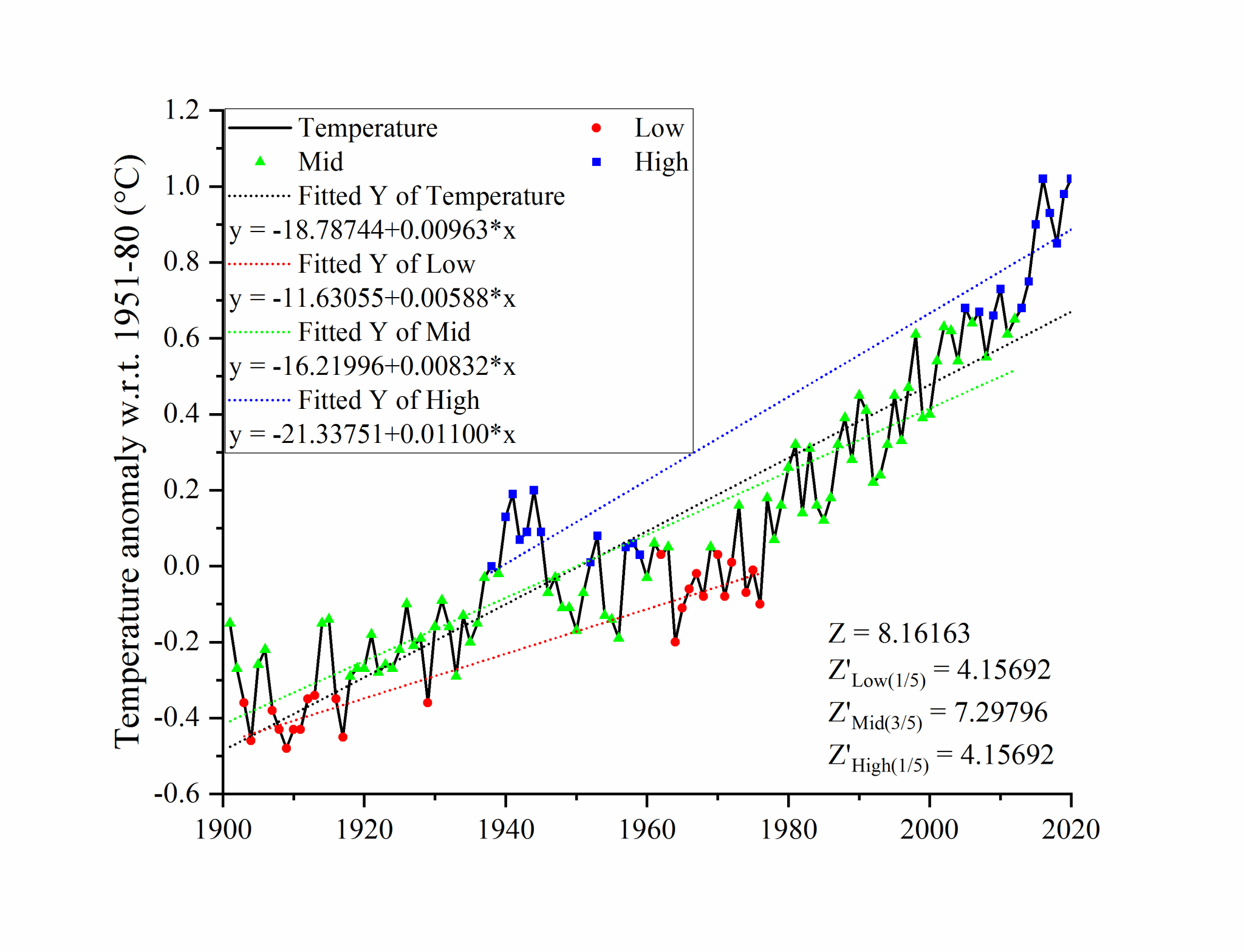
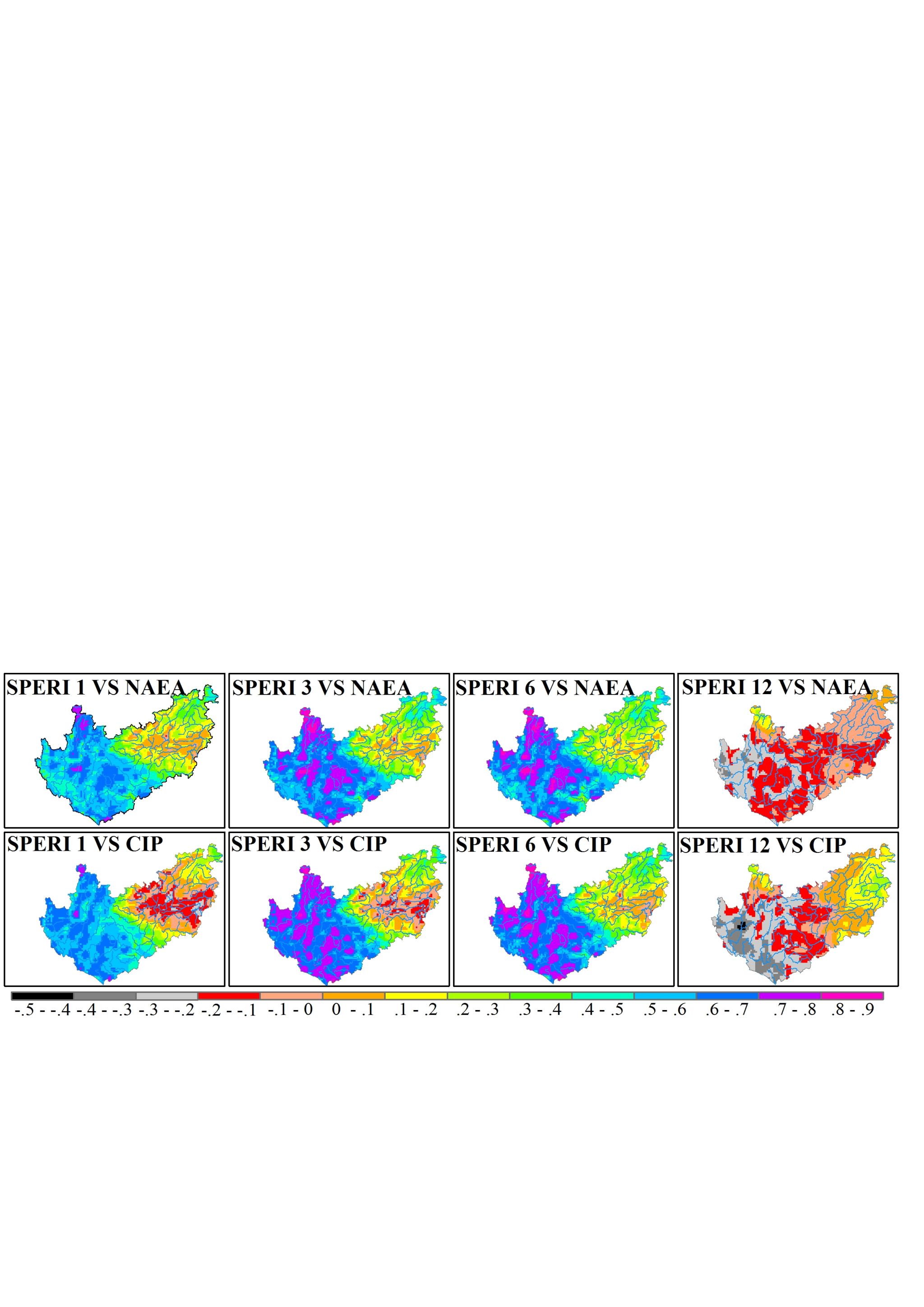
本站消息 受全球变化的影响,洪旱灾害受到广泛关注,包括云南在内的中国西南地区是全球干旱灾害频发区域,干旱机理、识别方法、评价模式等是其研究的重点。水利学院余航讲师、王龙教授以中国西南地区为研究区,首先从干旱机理出发,建立了区域和全球的干旱指标(文章1、2),从多时空尺度上解决了干旱识别率不高的问题,促进了干旱的深入认识;其次提出了一种新的序列内部结构检测的非参数统计方法(文章3),该方法不仅能够检测序列整体趋势,更能挖掘序列内部的模式特征;最后基于建立的方法,揭示了研究区干旱的地理分布规律(文章4、5),成果能够为研究区抗旱减灾、水资源配置提供决策参考。
上述工作得到了云南省科技厅的云南省农业节水工程技术研究中心、云南省基础研究计划等项目的资助。发表文章如下:
1、王龙, 余航*,等. A drought index: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration runoff index. Journal of Hydrology, 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.02.023.(TOP, IF=5.7)
2、 余航, 王龙*, 等. A global drought-aridity index: The spatiotemporal standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. Ecological Indicators, 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110484. (TOP, IF=6.9)
3、余航,王龙*,等.A non-parametric method to investigate internal trends in time sequence: A case study of temperature and precipitation, Ecological Indicators,10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.111373.(TOP, IF=7.0)
4、余航, 王龙*, 等. Hydrometeorological Drought Characteristics and Their Relationship With SST and Climate Indexes in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China—Based on the Improved SPERI,IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,10.1109/TGRS.2024.3432828.(1区, IF=7.5)
5、范德芳#, 余航#,王龙*,等. Effect of urbanization on the long-term change in pan evaporation: A case study of the Nanpan River Basin in China. Ecological Indicators, 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109631. (TOP, IF=6.9)